Non-terrestrial networks (NTN) are wireless communication systems that operate above the Earth’s surface, involving satellites at low Earth orbit (LEO), medium Earth orbit (MEO) and geostationary orbit (GEO), high-altitude platforms (HAPS) and drones. Such components are essential to realizing seamless coverage, bringing coverage even to remote areas that do not have access to traditional terrestrial networks.
Today, devices are separated into those connected to the 3GPP terrestrial network and those connected to satellite. In other words, users that require satellite connection need another device alongside their existing smartphone. With NTN, all mobile devices will be connected to both terrestrial and satellite networks as part of the 3GPP ecosystem. And as the technology continuously evolves, the satellites will become the base stations.
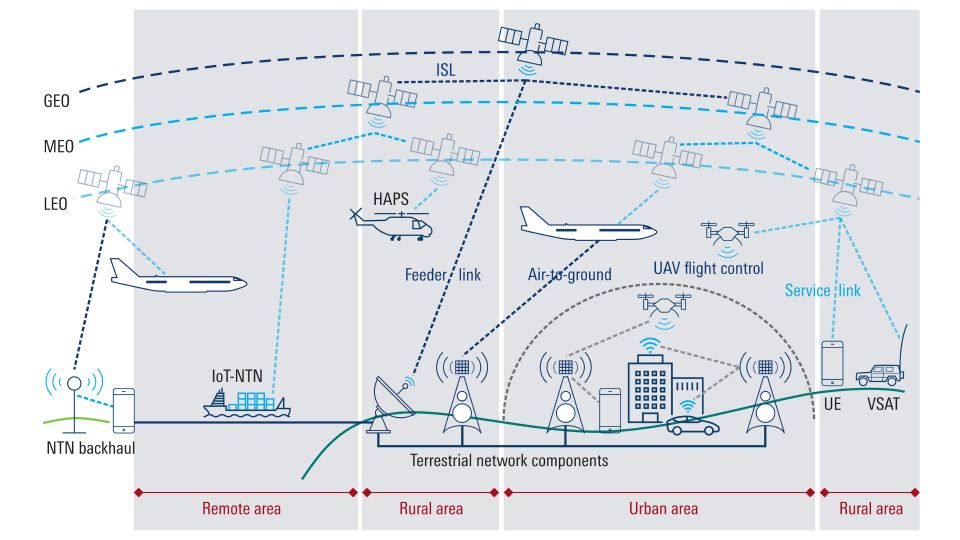
General connectivity overview of non-terrestrial networks
Open Lightbox
NTN has two aspects: NTN-IoT and NTN-NR. Each address different use cases and markets.
The NTN market has started establishing itself with NTN-IoT. NTN-IoT expands the reach of IoT use cases, enabling true global coverage over land, sea and air. It operates at both GEO and LEO altitudes, but current services mostly operate at GEO.
With the growth of NTN technology, NTN-NR will become increasingly relevant. NTN-NR will directly link smartphones and other 5G devices such as devices using RedCap for non-terrestrial services. It will operate at the LEO altitude and enable low data services, voice and messaging for various use cases.
Over the next five to ten years, we will see a growth in NTN-IoT satellite-based services.
· SOS and two-way messaging: Devices (smartphones, wearables and cars) can implement NTN NB-IoT chipsets to allow SOS and two-way messaging in areas with no terrestrial access.
· Agriculture and farming: Agricultural applications, such as precision farming and livestock monitoring, are possible even in rural or remote locations.
· Asset tracking: The location of valuable assets, such as shipping containers or vehicles, can be tracked even when the assets travel through areas with limited cellular connectivity.
· Disaster response and recovery: IoT devices for search and rescue, damage assessment and emergency response can be used in areas that have limited or no connectivity due to damaged infrastructure.
· Remote monitoring: Equipment in remote locations, such as oil rigs or weather stations, can be monitored.
· Maritime/airtime applications: Vessel tracking or environmental monitoring is possible in the open ocean or coastal areas with limited connectivity.
As NTN evolves, NTN-NR will increase in importance. This technology will extend the scope of NTN, providing services similar to that of NTN-IoT but at a much greater scale.
· Ubiquitous continuity of 5G basic services: With NTN's extended coverage and reach, the continuity of 5G basic services can be ensured ubiquitously. This implies seamless access to services like mobile data, voice calls and messaging, regardless of geographical location or terrain. This not only benefits individual users but also empowers businesses and industries that rely heavily on uninterrupted connectivity.
· 5G fixed wireless access (FWA) enhancement by NTN: By leveraging NTN, 5G FWA can be made more robust and employed more extensively. This can help in providing high-speed, stable internet services to households and businesses, particularly in areas where traditional wired connections are not viable or cost-effective.
· IoT revolution with 5G and NTN: The integration of NTN in 5G networks can significantly enhance IoT capabilities. This supports more efficient data exchange, improved device interoperability and the creation of sophisticated IoT ecosystems, driving digital transformation across industries.
· Automotive industry transformation: NTNs can facilitate the evolution of the automotive industry, supporting enhanced vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, autonomous vehicle development and advanced telematics services. This can greatly enhance safety, efficiency and user experience in the automotive sector.
· 5G simplified roaming solutions: NTNs can help implement simplified 5G roaming solutions. This allows for seamless, borderless connectivity, facilitating consistent and high-quality network services, regardless of location.
· 5G network backhaul support: NTNs can serve as an effective backhaul solution for 5G networks. This can help extend network reach, improve capacity and ensure reliable connectivity even in remote or difficult-to-reach areas.
· Public safety operations enhancement: NTNs can provide robust and reliable communication vital to public safety agencies. This can allow for real-time coordination, swift response and seamless information exchange, even in challenging environments or under strained infrastructure.
· Disaster response and recovery management: Natural or man-made disasters can compromise terrestrial networks. NTNs can fill this gap, providing crucial connectivity for disaster response teams, supporting the coordination of rescue operations and aiding in the swift recovery of affected regions.
· Advanced maritime and airtime connectivity: By leveraging NTN capabilities, connectivity can be significantly improved in maritime and airtime environments. This can enhance navigation, tracking and communication capabilities, driving safety and operational efficiency in these traditionally underserved areas.